Bruises on the Body: Simple Trauma or Sign of a Serious Problem?
Bruises are an integral part of our daily lives. They appear at the most unexpected moments and often make us wonder how we got them.
Although they may seem harmless bruises can tell us a lot about the state of our body. They are a signal that something has happened beneath the surface of our skin - whether it's a minor injury, a lack of certain nutrients or a more serious health problem.
Table of Contents
Bruises are often a source of curiosity:
- Why are some people more susceptible to them than others?
- Why do their colors change over time?
In this article we will look at all aspects of bruises, explain why they appear and how to most effectively deal with them. We will try to answer the questions that many of us ask ourselves when we see a blue-violet spot on our skin.
1. What are Bruises?
Bruises are a type of soft tissue injury under the skin. When a strong blow or pressure occurs the blood vessels in the affected area rupture without forming an open wound.
This causes blood to leak into the surrounding tissues where it remains encapsulated. It is this accumulation of blood that gives the bruise its characteristic color.
Bruises are not always the result of obvious trauma - they can also occur due to internal factors such as weakness of the vessel walls or circulatory disorders.
The size and intensity of the bruise depend on several factors:
- the force of the impact;
- the location of the injury;
- the person's individual tendency to bruise.
Areas with thinner skin, such as the hands or feet, often show bruises more clearly because the blood vessels are closer to the surface. Bruises can be a useful indicator of our health if we know how to interpret them.
2. Causes of Bruises
Bruises can occur due to a variety of factors ranging from simple injuries to more serious health problems.
Impacts or injuries
This is the most common cause of bruising. When you get hit, blood vessels in your skin rupture causing blood to pool in the affected area. Even a small bump can cause a large bruise if the area is sensitive.
Damaged or weak blood vessels
As we age or with certain health conditions the walls of blood vessels can become more fragile, increasing the likelihood of them rupturing with minimal stress.
Vitamin deficiency
Deficiencies in vitamins C and K significantly increase the risk of bruising. Vitamin C is important for the strength of connective tissue and vitamin K is essential for proper blood clotting.
Taking certain medications

Medications such as aspirin, anticoagulants or steroids can reduce blood clotting which increases the likelihood of bruising from even minor injuries.
Diseases
Diseases such as hemophilia, leukemia or chronic anemia can lead to frequent and unexplained bruising. They are often a sign of problems with clotting or blood cell production.
In addition to the above reasons, stress and fatigue can also affect the body's ability to deal with minor injuries. Chronic stress weakens the immune system and increases the skin's susceptibility to bruising.
Any unexplained or frequent cases of bruising should be discussed with a medical professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
3. How do Bruises Develop?
Bruises not only change color over time but also go through a complex healing process. The length of time it takes can vary by age - younger people with good circulation usually recover faster, while older people may take longer.
1. Initial stage
The bruise is red or pink. This is due to fresh blood that has leaked under the skin. This stage begins immediately after the injury and can last from a few hours to a day.
2. Middle stage
After a few days, the color turns blue or purple. This happens because the hemoglobin, which gives blood its red color, begins to break down into other substances such as bilirubin and biliverdin.
3. Final stage
The bruise will turn yellow or green as the body absorbs the spilled blood. This process can take several days or weeks depending on the size of the bruise and the individual's speed of recovery.
If a bruise remains painful or unchanged for a long period of time, it may be a sign of a more serious problem such as an infection or serious injury that requires medical attention. It is important to monitor how your bruise develops and consult a doctor if anything concerns you.
4. How to Treat Bruises?
Treatment for bruises involves a combination of methods to relieve pain, reduce swelling and speed up recovery.
- Use ice: Apply a cold compress immediately after the injury to reduce swelling and slow bleeding. Ice should be wrapped in a towel to avoid direct contact with the skin;
- Raise the affected area above the level of the heart: This helps blood drain from the area faster and reduces swelling;
- Do not put pressure on the area: Avoid putting pressure on the affected area to give the tissues time to recover;
- Use ointments and gels: Use special products containing Arnica, vitamin K or Heparin. These can speed up the healing process.
In addition to the methods already listed for dealing with bruises, homemade recipes can also be an excellent way to relieve bruises. They are easy to prepare, but if you don't have the time to make them yourself you can try our Ointments for Bruises.
1. Homemade Arnica Ointment
Required ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons dried Arnica flowers (or 1 tablespoon Arnica powder);
- 1/2 cup Coconut oil or olive oil;
- 1 tablespoon beeswax (grated or granulated);
- 5-10 drops of Lavender essential oil (optional, for a calming effect);
- Clean glass storage jar.
How to make it:
- In a small bowl, heat the Coconut oil or olive oil in a water bath;
- Add the dried Arnica and let it steep over low heat for about 30 minutes;
- Strain the oil using cheesecloth to remove any Arnica residue;
- Add the grated beeswax to the strained oil and return the bowl to the water bath. Stir until the wax is completely melted;
- Once the mixture has cooled slightly, add the Lavender essential oil;
- Pour the finished ointment into a clean glass jar. Let it cool and set completely before closing the lid;
- Apply a small amount of the ointment to the bruise or affected area 2-3 times a day.

2. Turmeric and Honey Mask
Required ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon Turmeric powder;
- 1 tablespoon Honey.
How to make it:
- Mix the Turmeric and Honey until a homogeneous mixture is obtained;
- Apply the mixture to the bruise and leave for about 20 minutes;
- Wash properly with lukewarm water.
3. Apple cider vinegar compress
Required ingredients:
- Equal parts apple cider vinegar and water.
How to make it:
- Mix apple cider vinegar and water in a small bowl;
- Soak a clean cloth in the mixture and apply it to the bruise for 15-20 minutes.
4. Chamomile tea
Required ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon of dried Chamomile flowers ( or 1 tea bag);
- 1 cup of water.
How to make it:
- Steep Chamomile in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Let it cool;
- Soak a cotton ball in the liquid and apply it to the affected area.
5. Onion paste
Required ingredients:
- 1 small onion;
- 1 pinch of salt.
How to make it:
- Grate the onion on a fine grater and mix it with the salt until you get a homogeneous mixture;
- Apply the mixture to the bruise and cover with gauze for 30 minutes.
If the bruise does not improve after home treatment or becomes more painful, it is advisable to seek medical attention. It is important to listen to your body's signals and respond in a timely manner.
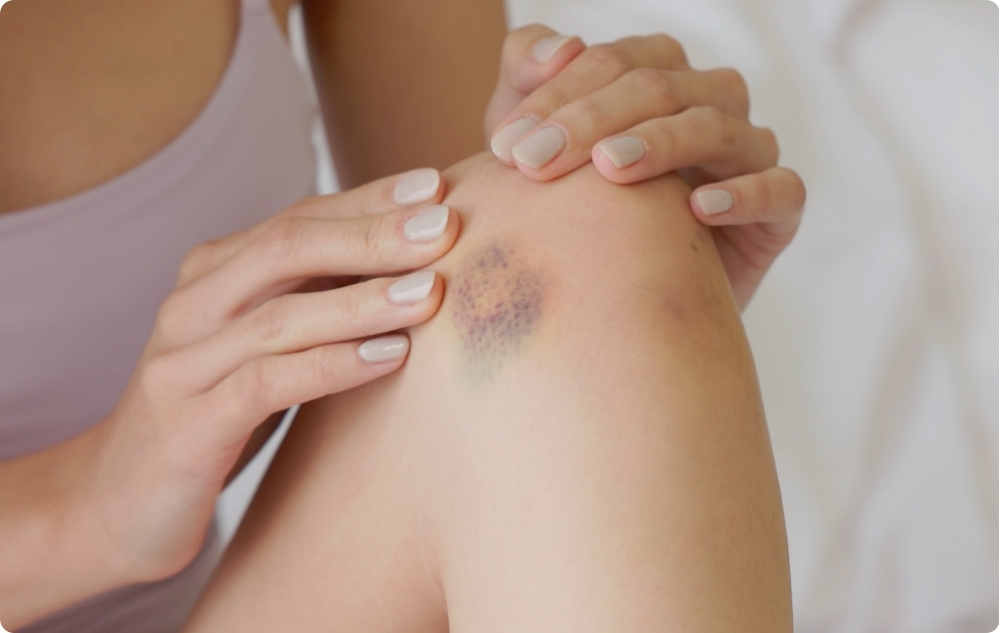
5. When are Bruises a Sign of a More Serious Problem?
Although most bruises are harmless, sometimes they can be a warning sign of a more serious health problem.
Here are a few cases you should pay attention to:
Bruises that appear for no reason
If you notice that you are getting bruises without having injured yourself it could be a sign of blood clotting problems or a deficiency in certain nutrients.
Frequent or unusually large bruises
If you constantly get bruises or they are larger than usual these may be signs of conditions such as thrombocytopenia or other blood disorders.
Bruises that don't go away
Bruises usually start to fade after a few days. If the bruise remains unchanged for more than a month you should consult a doctor.

Bruises accompanied by unusual symptoms
If bruising is accompanied by bleeding gums, frequent nosebleeds or other unusual symptoms, it may be a sign of diseases such as hemophilia or leukemia.
What to do if you notice any of these signs?
- See a doctor: If you have any of the above symptoms, be sure to see a medical professional. Early diagnosis can prevent complications;
- Watch for other changes: In addition to bruising pay attention to other symptoms such as fatigue, weakness or weight loss;
- Keep notes: If you bruise frequently, write down when and where they appear. This can help your doctor identify the problem;
- Get tests: A complete blood count test, blood clotting tests and vitamin levels tests are essential steps in clarifying the cause of your bruising.
6. How to Prevent Bruises?
Careful body care, healthy eating and caution in everyday life are key factors in preventing unwanted bruises.
Here are some specific actions you can take:
Drink enough water
Hydration improves blood circulation and strengthens tissues which reduces the risk of damage.
Keep your skin hydrated
Hydrated and nourished skin is more resistant to damage. Use moisturizers and avoid excessive sun exposure.
Consume foods rich in vitamins
To strengthen blood vessels consume more foods rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, peppers, broccoli) and vitamin K (green leafy vegetables, broccoli, Brussels sprouts).
Wear protective gear
Wear appropriate protective equipment such as knee pads, elbow pads or specialized clothing if you practice contact sports or activities where there is a high risk of falls and impacts.
Be careful with medications
If you are taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin or anticoagulants consult your doctor regularly.
Wear comfortable clothes
Wear comfortable clothing that does not put excessive pressure on the skin and blood vessels. Clothing that is too tight can increase the risk of pressure and subsequent bruising.
7. Conclusion
Bruises are a common problem that many people experience in their daily lives. While in most cases they are harmless and the result of minor injuries, sometimes bruises can be a sign of more serious health conditions such as blood clotting disorders, vitamin deficiencies or even blood diseases.
It is important to recognize when bruises are simply part of the body's normal functioning and when they require more in-depth attention. Regular health care, a balanced diet and paying attention to our body's signals help us not only cope with bruises but also prevent possible complications.
If bruises are unusual, frequent or last a long time, don't hesitate to consult a specialist.
SOURCES:
1. WebMD: What Are Bruises? What Causes Them? (11.02.2025)
2. Healthline: What Can Cause You to Bruise Easily? (11.02.2025)











