Fighting Acne: How to Achieve Clean and Healthy Skin

Acne is one of the most common skin conditions. Although it is usually associated with the teenage years Acne can occur in both childhood and adulthood.
It can range from mild, temporary pimples to severe, chronic conditions that require medical intervention.
In this article we will take a detailed look at the causes of its appearance, the types of Acne, methods of treatment and prevention as well as how proper skin care and a healthy lifestyle can contribute to healthier and clearer skin.
Table of Contents
1. What is Acne?
Acne is a chronic skin disease that affects the sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
Our skin contains millions of tiny pores that allow sebum (the oil produced by the sebaceous glands) to come to the surface and keep the skin hydrated and protected.
When these pores become clogged with excess sebum, dead skin cells and bacteria, conditions are created for inflammation and the appearance of Acne.
How does Acne form?
The process of Acne formation goes through several stages:
- Increased sebum production - the sebaceous glands begin to produce excessive amounts of oil, which creates a favorable environment for the accumulation of dirt;
- Clogging of the pores - excess sebum combines with dead skin cells, forming a plug that blocks the pores;
- Bacterial growth - the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes accumulate in the clogged pores which is normally present on the skin, but when overgrown, it causes inflammatory reactions;
- Inflammation and lesion formation - when the immune system reacts to the accumulation of bacteria redness, swelling and the formation of various types of pimples occur.
In which areas of the body does it appear most often?
Acne usually affects areas with a high concentration of sebaceous glands:
- Face - the forehead, nose and chin (T-zone) are the most commonly affected areas;
- Back - common in men as the skin there is thicker and the sebaceous glands are more active;
- Chest - hormonal changes can lead to Acne in this area as well;
- Shoulders and neck - sweat, rubbing against clothing and carrying backpacks can cause Acne in these areas.
Acne is often confused with other skin conditions such as rosacea, folliculitis or seborrheic dermatitis.
2. Main Causes of Acne
Acne is caused by a combination of internal and external factors that affect the skin and lead to clogged pores and inflammation.
Understanding these factors is key to its effective prevention and treatment.
1. Hormonal changes
Hormones play a leading role in the development of Acne. They stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum which increases the likelihood of clogged pores and the formation of pimples.
- Puberty - during adolescence, androgen levels (male hormones that are also found in women) increase leading to an overproduction of sebum;
- Pregnancy - hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause Acne to worsen or cause Acne to appear in women who have not had Acne before;
- Menstrual cycle - many women experience a worsening of Acne before or during menstruation due to fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) - this hormonal disorder can lead to chronic Acne along with other symptoms such as irregular periods and increased hair growth.
2. Genetic predisposition
If your parents had severe Acne there is a high probability that you will suffer from it too.
- Size and activity of the sebaceous glands - some people are genetically predisposed to larger and more active sebaceous glands;
- Prone to inflammation - the immune system in some people reacts more aggressively to bacteria, leading to more severe forms of Acne;
- The way the skin regenerates - dead skin cells are not shed effectively, leading to clogged pores.
3. Stress and psychoemotional factors
Stress itself does not cause Acne, but it can worsen the condition by increasing levels of cortisol, a hormone that stimulates sebum production.
- Chronic stress - long-term stress increases inflammation in the body and weakens the immune system;
- Lack of sleep - insufficient sleep also increases cortisol levels and can lead to more frequent breakouts;
- Emotional disorders - depression and anxiety can worsen skin conditions by increasing oxidative stress and inflammation.
4. Improper skin care
An improper skin care routine can contribute to the appearance of Acne:
- Use of comedogenic products - some cosmetic products contain oils and ingredients that clog pores;
- Excessive facial cleansing - aggressive washing and exfoliation can lead to dryness and a reactive increase in sebum;
- Lack of hydration - dehydrated skin often produces more oil to compensate for the lack of moisture;
- Improper makeup removal - if makeup is not completely removed pores can become clogged, leading to the formation of Acne.
5. Nutrition and diet
Although Acne is not directly caused by food, certain foods can contribute to worsening the condition:
- Processed carbohydrates and sugar - increase insulin levels which stimulates sebum production;
- Dairy products - studies show that dairy products can affect hormones and worsen Acne;
- Fatty and fried foods - can increase the inflammatory processes in the body;
- Lack of healthy fats - Omega-3 fatty acids (from fish, flaxseed, walnuts) help reduce inflammation.
6. Environmental factors
Environmental factors also play a role in the development of Acne:
- Air pollution - dirt particles and toxins can clog pores and cause inflammation;
- Humidity and sweating - warm and humid climates can lead to clogged pores;
- Sun exposure - although the sun can temporarily dry out pimples it also stimulates sebum production and can lead to worsening Acne.
7. Medications and hormonal therapies

Some medications can cause or worsen Acne:
- Corticosteroids - steroid use can lead to hormonal changes and the appearance of Acne;
- Antidepressants - some psychiatric medications can cause skin changes;
- Contraceptives - some types of hormonal contraceptives improve Acne but others can worsen it.
3. Types of Acne
Acne is not a uniform condition - it can manifest itself in different forms and degrees of severity. Depending on the type of lesions, their location and the intensity of inflammation, Acne can be classified into several main types.
Non-inflammatory Acne
This type of Acne is characterized by the presence of clogged pores but without significant inflammation.
- Blackheads (open comedones) - form when pores become clogged with sebum and dead skin cells but remain open;
- Whiteheads (closed comedones) - pores are clogged but remain covered by a thin layer of skin, making the lesion white or skin-colored. They are more difficult to remove and can easily become inflamed.
Inflammatory Acne
This type of Acne involves red, swollen and painful lesions caused by bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Papules - small, red bumps that form when the walls of the pores become irritated and inflamed. They are hard to the touch and do not contain pus;
- Pustules - look like papules but contain pus in the center. They are usually red at the base with a white or yellow head.
Deep and severe Acne
These forms of Acne affect the deeper layers of the skin and can lead to scarring.
- Nodules - large, hard, painful lumps under the skin that occur when hair follicles become deeply inflamed. They do not contain pus and cannot be squeezed out;
- Cystic Acne - the most severe form of Acne. It is large, pus-filled lesions that develop deep within the skin. This type of Acne often leaves scars and requires medical treatment.
Specific types of Acne
In addition to the traditional forms of Acne, there are several specific types that are caused by various external and internal factors.
- Acne Mechanica - caused by friction, pressure or irritation of the skin (for example, from tight clothing, helmets, backpacks or mobile phones);
- Hormonal Acne - occurs most often in women and appears around the chin, jaw and lower face, often associated with the menstrual cycle or hormonal disorders;
- Cosmetic Acne - occurs as a result of the use of comedogenic cosmetics that clog pores;
- Adult Acne - can appear even after the age of 30, often associated with stress, improper skin care or internal health problems;
- Drug Acne - caused by certain medications such as corticosteroids, antiepileptic drugs and some antidepressants.
4. How to Treat Acne?
Acne treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the type of lesions and the individual characteristics of the skin. There are various methods for dealing with Acne - from topical products and medications to professional dermatological procedures.
The approach must be personalized and tailored to the specific needs of the patient:
1. Local treatment
Topical agents are used for direct application to the affected areas and are effective for mild to moderate Acne.
- Benzoyl peroxide - one of the most popular ingredients for treating Acne. It has antibacterial properties and reduces inflammation. It is often used for papulopustular Acne;
- Salicylic acid - helps unclog pores and exfoliate dead cells. It is suitable for people with comedonal Acne;
- Azelaic acid - has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties and also reduces post-Acne pigmentation;
- Topical retinoids (retinol, adapalene, tretinoin) - stimulate skin renewal and prevent pore blockage. They are used for various types of Acne including blackheads and inflammatory lesions;
- Antibacterial creams and gels (clindamycin, erythromycin) - they are used to control bacterial infection in the skin and reduce inflammation.
2. Oral treatment
In more severe cases of Acne medication may be required.
- Antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline, tetracycline) - inhibit the growth of the Propionibacterium acnes bacteria and reduce inflammation. They are prescribed for short-term use to avoid developing antibiotic resistance;
- Oral retinoids (isotretinoin) - the most effective treatment for severe cystic Acne. They reduce sebum production, shrink sebaceous glands and prevent the formation of new lesions. Requires close medical supervision due to potential side effects;
- Hormonal therapies (oral contraceptives, spironolactone) - combined birth control pills are used for hormonal Acne, which regulate androgen levels and reduce sebum secretion.
3. Professional dermatological procedures
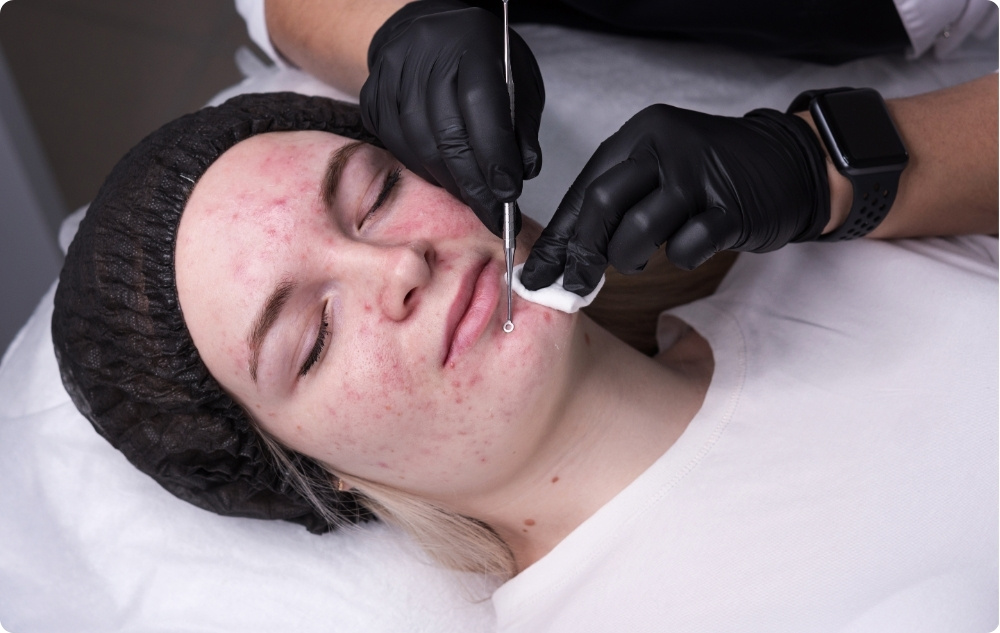
Dermatological therapies can improve skin condition, especially if traditional methods do not work.
- Chemical peeling - uses acids (glycolic, salicylic, lactic) to remove the top layer of the skin and stimulate its renewal. Helps with comedones and mild inflammatory Acne;
- Laser therapy and light procedures - lasers destroy bacteria and reduce inflammation and blue light has an antiseptic effect. They are suitable for people with moderate to severe Acne;
- Microneedling - a procedure in which small needles pierce the skin, stimulating its natural regeneration. It is used to treat Acne scars;
- Drainage and extraction - a specialized procedure in which a dermatologist mechanically removes clogged pores and cysts. It should only be performed by a professional to avoid infections and scars.
4. Lifestyle changes
Acne treatment doesn't just involve medication and cosmetics. Lifestyle also plays an important role in controlling the condition.
- Proper skin care - regular cleansing with gentle products, use of non-comedogenic cosmetics and sun protection help prevent Acne from worsening;
- Stress management - physical activity and sufficient sleep can help reduce stress levels, which can negatively affect the condition of the skin;
- Nutrition - avoiding sugar, processed foods and dairy products, as well as consuming foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 can help reduce inflammation in the body;
- Physical activity - regular exercise improves blood circulation and helps to clear toxins from the body, but it is important to cleanse the face thoroughly after exercise to avoid clogging the pores.
5. Home Remedies for Dealing with Acne
Home remedies for Acne are a popular choice for people who prefer natural methods or want to complement traditional treatment.
Many natural ingredients have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help reduce inflammation and speed up skin healing.
Useful natural ingredients against Acne
Various natural products can help reduce Acne by acting on the root causes of its appearance - excessive oiliness, inflammation and bacterial growth:
- Tea Tree Oil has strong antibacterial properties and helps reduce inflammation;
- Aloe Vera soothes irritated skin, reduces redness and helps lesions heal faster;
- Honey and cinnamon - this combination has antibacterial effects and can help cleanse pores;
- Apple cider vinegar balances the skin's pH levels and helps control sebum secretion;
- Green tea contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can soothe the skin and reduce redness;
- Oatmeal helps exfoliate the skin, absorbs excess sebum and soothes irritation;
- Lemon juice has antiseptic properties, but should be used with caution as it can dry out the skin and increase its sensitivity to the sun.
Home remedies for treating Acne
1. Cleansing mask with Honey and Cinnamon
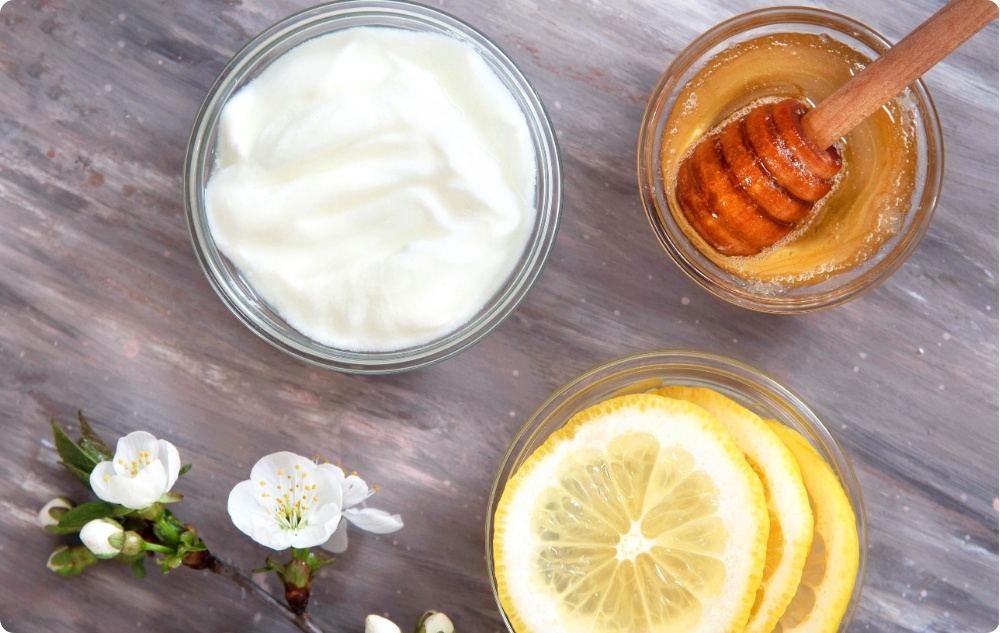

Required ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon Honey;
- ½ teaspoon Cinnamon.
How to make it:
- Mix honey and cinnamon in a small bowl until you get a smooth paste;
- Apply a thin layer to cleansed skin;
- Leave on for 10-15 minutes;
- Rinse with warm water and pat dry with a soft towel;
- Apply 1-2 times a week.
2. Soothing tonic with Apple Cider Vinegar
Required ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon Apple Cider Vinegar;
- 3 tablespoons filtered water;
- 3-4 drops Tea Tree oil (optional).
How to make it:
- Mix the ingredients in a glass bottle;
- Shake well before use;
- Apply with a cotton pad to the face, avoiding the eye area;
- Let it absorb and then apply a moisturizer.
3. Oatmeal face mask
Required ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons of fine rolled oats;
- 1 tablespoon of yogurt;
- 1 teaspoon of lemon juice.
How to make it:
- Mix all ingredients until a paste is formed;
- Apply to face and leave for 15 minutes;
- Massage gently, then rinse with lukewarm water.
Tips for using home remedies for Acne
- Always do an allergy test on a small area of skin before first use;
- Do not use lemon juice during the day if you are not going to apply sunscreen;
- Home remedies are effective, but they cannot replace medical treatment for severe Acne.
6. Myths about Acne
There are many myths about Acne that can lead to improper treatment or even worsening of the condition.
Myth 1: Acne is caused by poor hygiene
Fact: Frequent face washing does not prevent Acne and may even make it worse.
Excessive facial cleansing, especially with harsh products, can lead to irritation and a reactive increase in sebum which can ultimately worsen Acne.
Myth 2: Sun exposure cures Acne
Fact: Although sunlight can temporarily dry out pimples, long-term sun exposure can worsen Acne.
The sun increases sebum production which can lead to new flare-ups after initial improvement.
Sunscreen protection (with a non-comedogenic formula) is important for people prone to Acne.
Myth 3: Only teenagers suffer from Acne
Fact: Acne can affect people of any age.
Acne is common in the teenage years but many adults also suffer from it, especially women who experience hormonal changes due to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy or menopause.
Stress and lifestyle can also trigger the appearance of Acne in adults.
Myth 4: Makeup causes Acne
Fact: Non-comedogenic cosmetics do not cause Acne, but inappropriate products can worsen the condition.
While some heavy and oily makeup can clog pores and worsen Acne, there are specialized products that are designed for Acne-prone skin.
Using “non-comedogenic” makeup and regularly removing it at the end of the day are key to maintaining healthy skin.

Myth 5: Only oily skin suffers from Acne
Fact: Acne can occur on any skin type, including dry and sensitive.
While oily skin is more prone to Acne due to overproduction of sebum, dry skin can also develop Acne, especially if overly aggressive cleansing products are used that disrupt the skin's barrier function.
Myth 6: Acne goes away on its own
Fact: In some cases, Acne may improve over time but in others treatment is required.
While some people only have Acne in their teenage years for others it can last for years and get worse if not treated properly.
Timely treatment can help prevent long-term scarring and psychological discomfort.
7. Conclusion
Acne is a skin problem that can be influenced by multiple factors - hormonal changes, nutrition, stress and improper skin care.
Appropriate treatment includes a combination of the right products, a healthy lifestyle and, if necessary, consultation with a dermatologist.
It is important to avoid self-medication methods which can worsen the condition.
SOURCES:
1. MayoClinic: Acne (04.04.2025)








